Knee joint arthrosis or osteoarthritis is a disease that occurs in the light of dystrophic changes, with further growth of connective tissue.There are many factors that affect the development of the disease, but all of them eventually cause disruption of cartilage metabolism.In medical literature, knee joint arthrosis is called gonarthrosis.
According to statistics, gonarthrosis occupies a leading position between other arthrosis.The disease brings severe discomfort that can suffer from pain while walking and resting.
Knowing early symptoms will contribute to the suspicion of the development of the pathology and at the initial stage of healing.
Causes
According to medical classification, there is primary and secondary gonarthrosis or arthrosis of the knee joint.
Knee joint arthrosis can occur in the wake of various diseases or act as a complication.When, due to an obscure history or clinical picture, it is impossible to determine the exact cause, gonarthrosis is called primary, but if the cause is known, then such arthrosis is called secondary.
Arthrosis develops with age in almost every person, on average, this period begins after 45-50 years of life.
The course of primary and secondary arthrosis and the pathogenesis are the same and does not depend on the cause of origin.
The most common causes of osteoarosis of arthrosis and knee joint are:
- Knee traumatic injury;
- Joint deformation internal and outdoors;
- Reduce one lower limb;
- Abnormal hypermobia of the joint;
- Chondroblast dysplasia;
- Certillary calcinosis;
- Osteomyelitis of the thigh and tibia;
- Rheumatoid arthritis or arthritis of any other etiology;
- Glucose metabolism;
- Metabolic diseases and hormonal diseases.
Injuries.After the knee injury in the joint cavity, inflammation may develop, which has a great deal of attention to alliteration.After the disappearance of pro -inflimatory agents, the processes of reparation or arthrosis are activated.
Most often, the disease occurs in the light of a fracture, with the breakdown of ligaments and damage to the cartilage surface of the bag and joint.
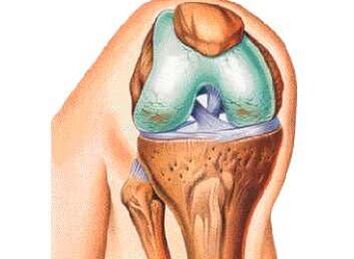
Congenital deformations.Deformation of Valgus or Varionor is found very often and without proper adjustments, sclerotic changes in the knee can be complicated.This is because one article falls more than it should be.
Reduce the lower extremities.As with deformations, in the pathogenesis of the disease, the inappropriate distribution of weight on the knees plays a role.
Knee hypermors.In this condition, the cartilage tissue of the knee joint can be applied to arthrosis by further degeneration and degeneration.Hypermson often causes spontaneous dislocation and spray of joint capsule.
Hand -haired dysplasia.Due to the inadequate development of the motor surface in the knee joint, the connective tissue is abnormal.
Calcinosis of the joint.The pathogenesis is based on the deposition of salts in the joint cavity and the production of specific precipitation, which results in calcification with subsequent osteoarthritis.
Osteomyelitis.Inflammatory bacterial disease in which the bones and joints are destroyed.First, anklosis and only then sclerosis is created.
Arthritis of any etiology.The most dangerous is rheumatoid arthritis, accompanied by autoimmune damage to the heart and joints.
Diabetes, like metabolic disorders, causes the flow of food to the joint and cartilage shoots.
Obesity.With the large weight of the body, large loads are on the knees when it is in the foot and standing.As a result of constant pressure, blood flow to the knee joints decreases and atrophy of dystrophy develops.
Symptoms
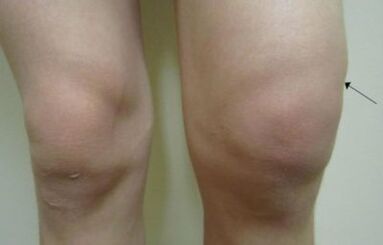
Symptoms of knee arthrosis depend on the stage of the abnormal process.On this basis, by analyzing their growth symptoms and tempo, you can evaluate the scale of cartilage tissue changes.
Symptoms of knee arthrosis:
- The presence of abnormal sounds during movement;
- Pain after loading or after rest;
- Reduction of functions;
- Swelling and joint growth;
- Abnormal dislocations, fractures and sublux;
- Temporary jam, which can occur during flexibility and expansion of the joint.
Clicks and crushes are not immediately observed and if they notice, they will not pay attention.Abnormal tunes are found to be the idea that the abnormal process by depositing salts or producing osteophytes becomes a cartilage gap.
Pain is due to the production of calcinates or osteophytes.Initially, the pain syndrome is not pronounced, later it only appears in the morning and passes after lunch, with the progression of the disease, the pain can occur during rest.
Decreased joint functions are manifested in the severity of the movements and their amplitude.Depending on the scene, the restrictions can last for some time and pass the rest.
Swelling occurs due to inflammation and hyperecretics of synovial fluid.There are also options when the skin is lit on the joints.Such symptoms can be scarlet fever or rheumatism.
Dislocation and sublux are due to the fact that the process relates to the bones and ligament of the knees.
Clushing is a condition in which movement in any axis is completely limited.Such a symptom indicates the process of neglecting the process and the need for difficult treatment.
The degree of arthrosis
Classification of osteoarthritis according to the following signs:
- Radiological symptoms;
- Clinical manifestations;
- Laboratory data.
The most common and convenient classification is radiological, it is simple and understandable, even without medical education.
On the basis of X -Rays, four degrees of arthrosis in the knee joint is distinguished:
- The joint gap reduction is small and there are no osteophytes;
- The interspoint gap is not impregnated, but there are signs of small calcinates or osteophytes;
- Interspoint Gap has a narrow expression, there are osteophytes, joint deformation begins;
- Joint gap, bone deformity, anklosis and dystrophy.
In relation to the clinical picture, the following stages are distinguished:
- Symptoms of mild quality are minor, are found in the morning and wake up after 30-60 minutes;
- Medium quality is a pronounced symptoms, discomfort passes before lunch, swelling is negligible, it progresses rapidly without treatment;
- Severe degree - characterized by persistent pain pain, discomfort during rest, morning firmness does not go through dinner, anklosis, bourgeois and knee joint.
Laboratory tests are provided, soy and leukocyte indicators are evaluated.It is also necessary to check the presence of rheumatoid factors.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of knee joint arthrosis is not difficult, but requires some skills from your doctor.
Two types of diagnostic measures are distinguished:
- Laboratory diagnosis;
- Instrumental diagnosis.
For the correct diagnosis, each method must be taken into account and analyzed the image as a whole.
Laboratory
If arthrosis is suspected, the attending physician will determine the following tests:
- General blood and urine test;
- Biochemical blood test;
- Determination of antibodies for rheumatoid factor;
- Determine antibodies on their own cells.
Laboratory data does not provide information at the stage of disease development.
Instrumental
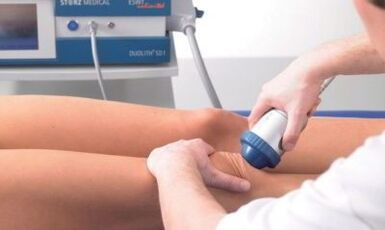
The instrumental diagnosis of arthrosis involves the following methods:
- Radiography in two standard forecasts;
- Minimum invasive arthroscopy;
- The test;
- CT;
- MRI;
- Scintigraphy (according to instructions).
Radiation diagnosis is intended to determine the changes in the joint and to assess the condition of the cartilage.
Treat
Knee joint arthrosis treatment is a long process.The duration of treatment is due to the fact that the compensation of cartilage tissue is very slow, and in some cases it is completely impossible to restore the joint.
Modern methods of treating arthrosis in the knee joint include comprehensive measures that are designed to remove inflammation, normalize lifestyle, and improve cartilage tissue metabolism.
There are such methods of therapy:
- Drug therapy;
- Exercise therapy and massage;
- Folk medicine;
- Surgical interventions.
The doctor will prescribe treatment on the basis of the duration of the disease, its developmental stage and clinical manifestations.
Medication
Drug therapy is aimed at alleviating pain and inflammatory reaction.For this purpose, the following medications are indicated:
- Non -anti -Anamals;
- Chondroprotectors;
- Glucocorticoid;
- Cytostatic.
The tablets from the knee joint arthrosis have many side effects.
Often, medications for arthrosis are prescribed for a long period, so the least toxic medications should be selected.
Exercises
Treatment of arthrosis using exercise therapy is aimed at strengthening the knee muscles and ligaments.With dosing of cartilage of the diseased joint, metabolism improves and regenerative processes are accelerated.
Exercises should be individually selected depending on the patient's disease and physical abilities.
Massage
Knee joint massage allows you to improve blood flow and relieve discomfort.Proper massage can prevent the appearance of anklosis and fake joints.
People
Knee joint arthrosis treatment should not be a major method of combating the pathology, or can only act as a drug addition.

Home treatments include:
- Reducing body weight;
- Normalization of labor hygiene and maintenance of day regimens;
- Fight against inflammation.
The antique effect has such herbs:
- Tincture from thyme and St. John's wort;
- Burdok leaves;
- White cabbage leaves;
- Infusions and decorations of dandelion and chamomile.
Operation
Surgery is prescribed by the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy or at the request of the patient.One of the main indications of surgical intervention is the 4th stage of the disease with radiological characteristics.
During surgery, surgeons can completely replace the joint with endoprosthesis or replace any part of it.

























